Storage Node
Introduction
The Docker container has the software you need to run your Storage Node.
Step 1. Download the Storage Node Docker Container
Step 2. Set up the Storage Node
The setup step must be performed only once. If a node has already been set up, running with the SETUP flag will result in failure.
A network-attached storage location may work, but this is neither supported nor recommended!
Splitting subfolders from the storage location (junctions, symlinks, hardlinks, etc.) will lead to a quick disqualification if they become unavailable! The writeability and readability checks are performed on the storage location, not on subfolders.
Linux Users: You must static mount via /etc/fstab. Failure to do so will put you in high risk of failing audits and getting disqualified. Here's how to do that: How do I setup static mount via /etc/fstab for Linux?
- Copy the command into a plain text editor like a
nano:
Replace the
<identity-dir>and<storage-dir>with your parameters.Copy the updated command.
Run it in a terminal window.
Your node has been set up!
Step 3. Run the Storage Node
Previous versions of the command that used the -v option rather than the --mount type=bind option will not work properly. Copy the updated command below.
- Copy the command into a plain text editor, like a
nano:
Edit the
WALLET,EMAIL,ADDRESS,STORAGEand replace the<identity-dir>, and<storage-dir>with your parameters.Copy the updated command.
Run it in a terminal window.
You're officially a Storage Node operator! 🎉
You can also check to see if the node was started properly by by running the following command in the terminal
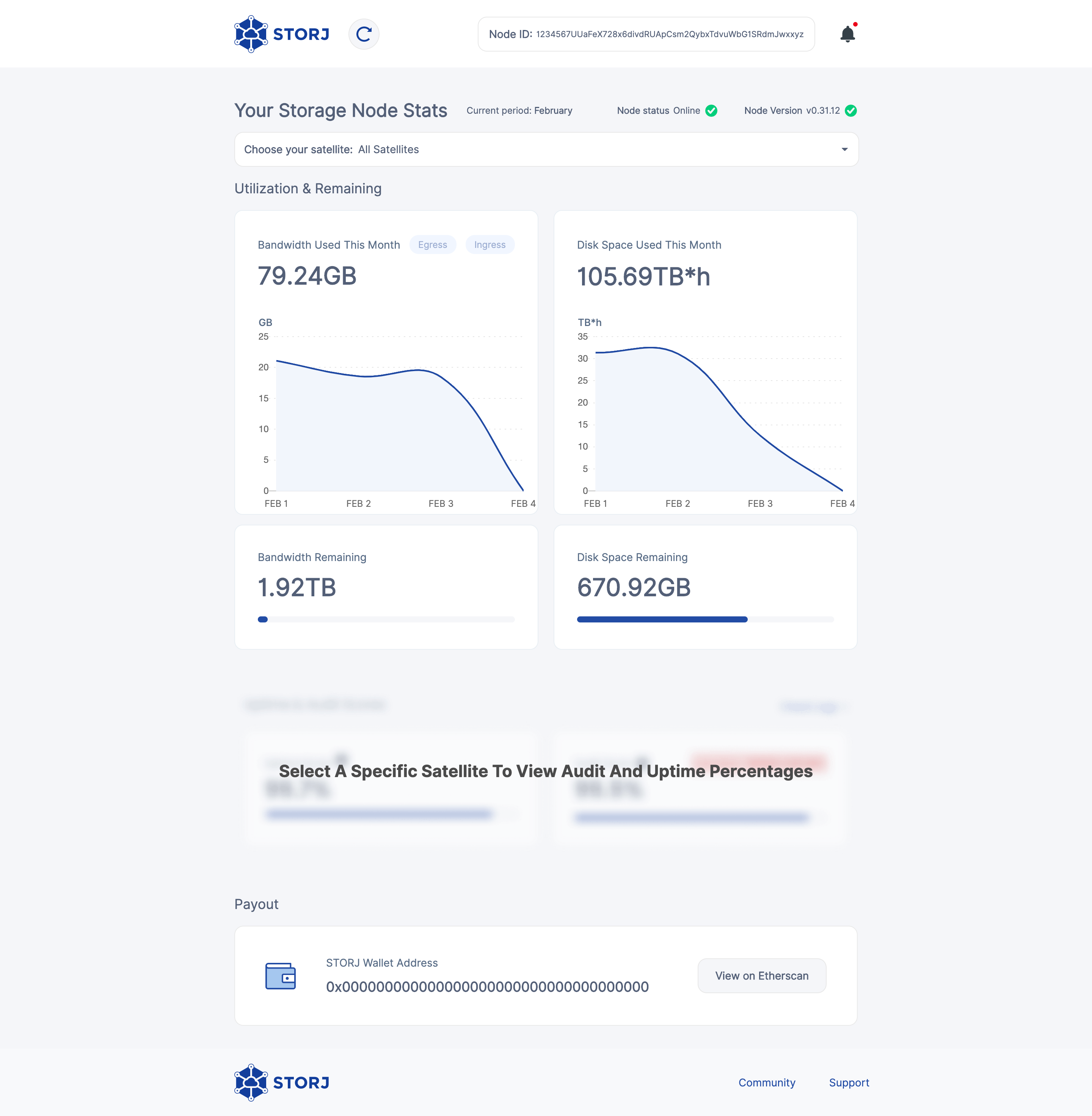
Step 4. Check the status of your node
You can check the status of your node, along with many other statistics by running the web Dashboard Windows. It will look like this: